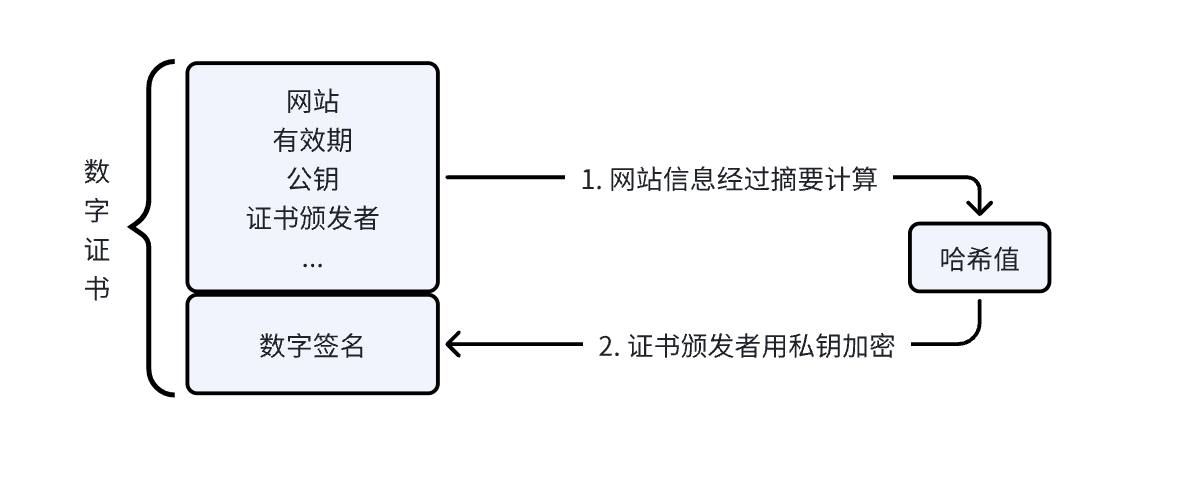
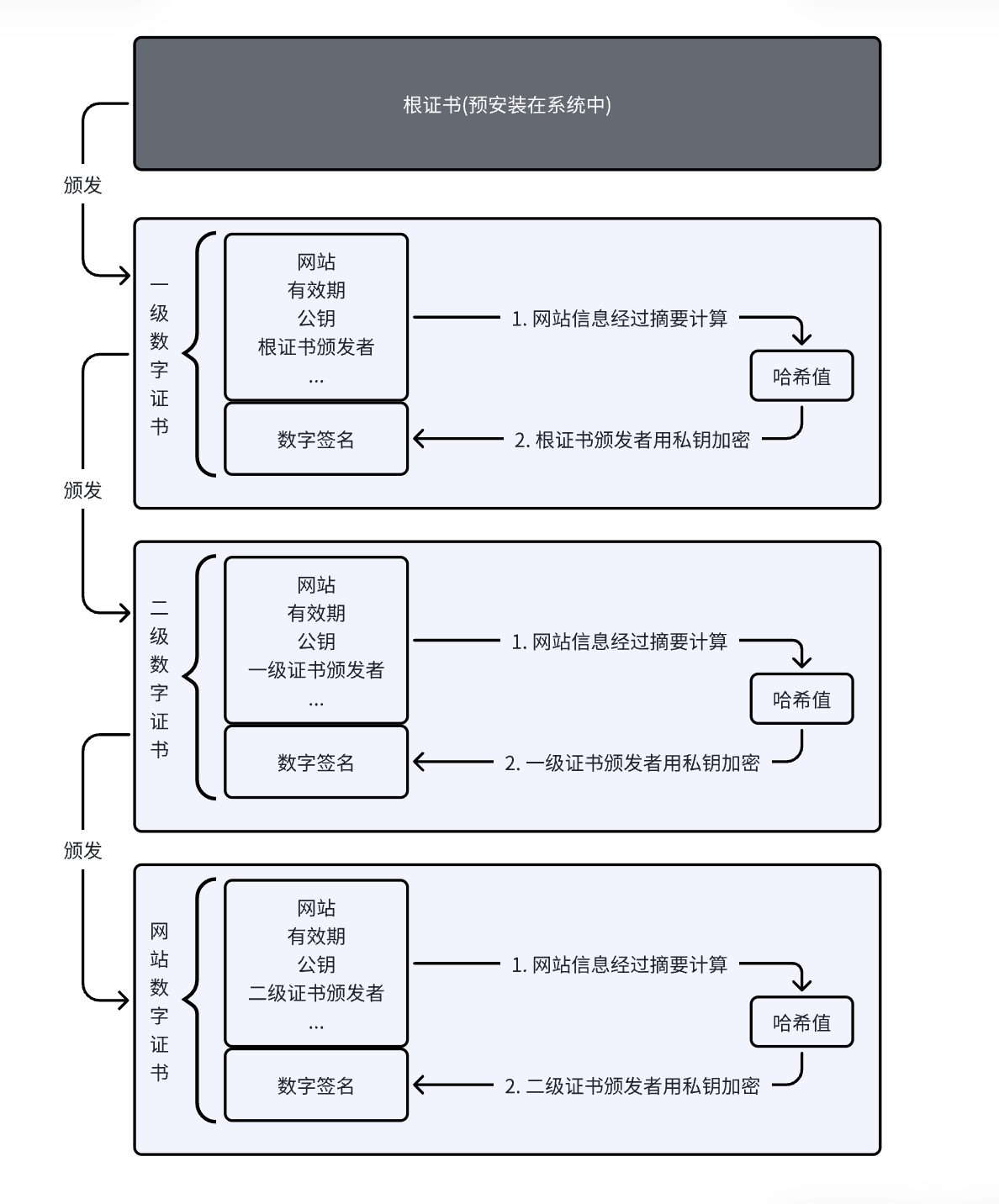
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ISspace(x) isspace((int)(x))
#define SERVER_STRING "Server: jdbhttpd/0.1.0\r\n"
void accept_request(int);
void bad_request(int);
void cat(int, FILE *);
void cannot_execute(int);
void error_die(const char *);
void execute_cgi(int, const char *, const char *, const char *);
int get_line(int, char *, int);
void headers(int, const char *);
void not_found(int);
void serve_file(int, const char *);
int startup(u_short *);
void unimplemented(int);
void accept_request(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
int numchars;
char method[255];
char url[255];
char path[512];
size_t i, j;
struct stat st;
int cgi = 0;
char *query_string = NULL;
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
i = 0; j = 0;
while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(method) - 1))
{
method[i] = buf[j];
i++; j++;
}
method[i] = '\0';
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") && strcasecmp(method, "POST"))
{
unimplemented(client);
return;
}
if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
cgi = 1;
i = 0;
while (ISspace(buf[j]) && (j < sizeof(buf)))
j++;
while (!ISspace(buf[j]) && (i < sizeof(url) - 1) && (j < sizeof(buf)))
{
url[i] = buf[j];
i++; j++;
}
url[i] = '\0';
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
{
query_string = url;
while ((*query_string != '?') && (*query_string != '\0'))
query_string++;
if (*query_string == '?')
{
cgi = 1;
*query_string = '\0';
query_string++;
}
}
sprintf(path, "htdocs%s", url);
if (path[strlen(path) - 1] == '/')
strcat(path, "index.html");
if (stat(path, &st) == -1) {
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
not_found(client);
}
else
{
if ((st.st_mode & S_IFMT) == S_IFDIR)
strcat(path, "/index.html");
if ((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) || (st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) || (st.st_mode & S_IXOTH) )
cgi = 1;
if (!cgi)
serve_file(client, path);
else
execute_cgi(client, path, method, query_string);
}
close(client);
}
void bad_request(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 400 BAD REQUEST\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<P>Your browser sent a bad request, ");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "such as a POST without a Content-Length.\r\n");
send(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
}
void cat(int client, FILE *resource)
{
char buf[1024];
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
while (!feof(resource))
{
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
}
}
void cannot_execute(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Server Error\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<P>Error prohibited CGI execution.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
void error_die(const char *sc)
{
perror(sc);
exit(1);
}
void execute_cgi(int client, const char *path, const char *method, const char *query_string)
{
char buf[1024];
int cgi_output[2];
int cgi_input[2];
pid_t pid;
int status;
int i;
char c;
int numchars = 1;
int content_length = -1;
buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0';
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
else
{
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))
{
buf[15] = '\0';
if (strcasecmp(buf, "Content-Length:") == 0)
content_length = atoi(&(buf[16]));
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
}
if (content_length == -1) {
bad_request(client);
return;
}
}
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
if (pipe(cgi_output) < 0) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
if (pipe(cgi_input) < 0) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
if ((pid = fork()) < 0 ) {
cannot_execute(client);
return;
}
if (pid == 0)
{
char meth_env[255];
char query_env[255];
char length_env[255];
dup2(cgi_output[1], 1);
dup2(cgi_input[0], 0);
close(cgi_output[0]);
close(cgi_input[1]);
sprintf(meth_env, "REQUEST_METHOD=%s", method);
putenv(meth_env);
if (strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0) {
sprintf(query_env, "QUERY_STRING=%s", query_string);
putenv(query_env);
}
else {
sprintf(length_env, "CONTENT_LENGTH=%d", content_length);
putenv(length_env);
}
execl(path, path, NULL);
exit(0);
} else {
close(cgi_output[1]);
close(cgi_input[0]);
if (strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
for (i = 0; i < content_length; i++) {
recv(client, &c, 1, 0);
write(cgi_input[1], &c, 1);
}
while (read(cgi_output[0], &c, 1) > 0)
send(client, &c, 1, 0);
close(cgi_output[0]);
close(cgi_input[1]);
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
}
}
int get_line(int sock, char *buf, int size)
{
int i = 0;
char c = '\0';
int n;
while ((i < size - 1) && (c != '\n'))
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
if (n > 0)
{
if (c == '\r')
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, MSG_PEEK);
if ((n > 0) && (c == '\n'))
recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = c;
i++;
}
else
c = '\n';
}
buf[i] = '\0';
return(i);
}
void headers(int client, const char *filename)
{
char buf[1024];
(void)filename;
strcpy(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
strcpy(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
strcpy(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
void not_found(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<HTML><TITLE>Not Found</TITLE>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>The server could not fulfill\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "your request because the resource specified\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "is unavailable or nonexistent.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
void serve_file(int client, const char *filename)
{
FILE *resource = NULL;
int numchars = 1;
char buf[1024];
buf[0] = 'A'; buf[1] = '\0';
while ((numchars > 0) && strcmp("\n", buf))
numchars = get_line(client, buf, sizeof(buf));
resource = fopen(filename, "r");
if (resource == NULL)
not_found(client);
else
{
headers(client, filename);
cat(client, resource);
}
fclose(resource);
}
int startup(u_short *port)
{
int httpd = 0;
struct sockaddr_in name;
httpd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (httpd == -1)
error_die("socket");
memset(&name, 0, sizeof(name));
name.sin_family = AF_INET;
name.sin_port = htons(*port);
name.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
if (bind(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, sizeof(name)) < 0)
error_die("bind");
if (*port == 0)
{
int namelen = sizeof(name);
if (getsockname(httpd, (struct sockaddr *)&name, &namelen) == -1)
error_die("getsockname");
*port = ntohs(name.sin_port);
}
if (listen(httpd, 5) < 0)
error_die("listen");
return(httpd);
}
void unimplemented(int client)
{
char buf[1024];
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 501 Method Not Implemented\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, SERVER_STRING);
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Method Not Implemented\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</TITLE></HEAD>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "<BODY><P>HTTP request method not supported.\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
sprintf(buf, "</BODY></HTML>\r\n");
send(client, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
}
int main(void)
{
int server_sock = -1;
u_short port = 0;
int client_sock = -1;
struct sockaddr_in client_name;
int client_name_len = sizeof(client_name);
pthread_t newthread;
server_sock = startup(&port);
printf("httpd running on port %d\n", port);
while (1)
{
client_sock = accept(server_sock,(struct sockaddr *)&client_name,&client_name_len);
if (client_sock == -1)
error_die("accept");
if (pthread_create(&newthread , NULL, accept_request, client_sock) != 0)
perror("pthread_create");
}
close(server_sock);
return(0);
}